In Arizona, the landscape between rural and urban medical clinics is strikingly different. If you’re a doctor or clinic owner in Arizona, you’ve probably felt that tug between the wide-open spaces of the desert and the buzz of city life. Selling a medical practice is about understanding how your spot on the map shapes everything from patient flow to the final sale price.
Table of Contents
ToggleKey Differences Between Rural and Urban Medical Clinics in Arizona
Arizona’s landscape tells a unique story when it comes to healthcare. What is the difference between rural and urban medical clinics? At its core, rural areas often run leaner, serving spread-out populations with a family doctor vibe, while urban ones juggle high volumes and specialist teams. But let’s peel back the layers.
1. Patient Demographics
In rural Arizona, patients may drive an hour just for a check-up, navigating dusty backroads and spotty cell service. Folks here tend to face tougher odds with everyday health battles.
The difference in access is also visible in claim activity trends across regions.
The chart below compares the percentages of medical claims for retail clinics between 2015 and 2020 for rural and urban settings. It illustrates how medical claim activity at retail clinics has evolved. Rural and urban clinics remained relatively close in percentages until 2019, when both experienced sharp increases. Urban clinics then slightly surpassed rural ones by 2020, showing faster growth in urban healthcare access through retail clinics.
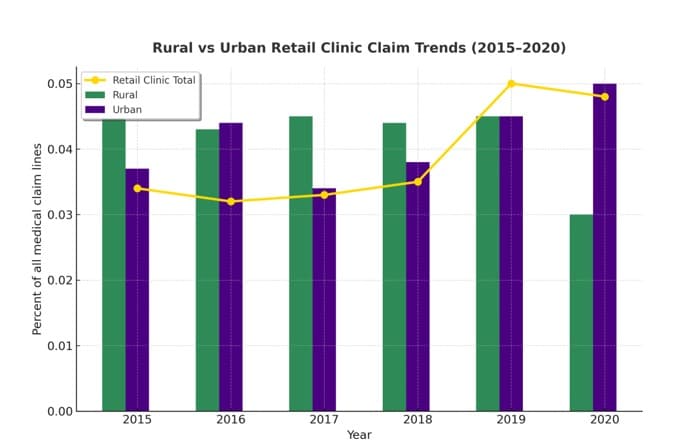
This pattern reflects how population density, infrastructure, and resource availability continue to shape the healthcare experience for patients in different parts of Arizona. Rural communities rely on fewer clinics spread across large distances, while urban residents increasingly turn to retail clinics for faster and more accessible care.
2. Common Health Issues
What health care problem is more common in rural areas compared to urban areas? Take chronic conditions like diabetes or heart disease; they hit rural residents harder, with rates climbing due to limited fresh food options and longer waits for specialists. Urban clinics, on the other hand, see a mix of quick visits from young professionals and diverse immigrant families seeking preventive care.
Obesity and related issues also stand out, fueled by economic strains and limited access to gyms. Urban areas counter with more wellness programs, but rural clinics often step up as community hubs, boosting their sales stories around impact.
3. Infrastructure and Technology Adoption
Now, let’s talk bricks and bytes. Rural clinics in Arizona lean on basics. At the same time, urban ones boast gleaming facilities with on-site laboratories and imaging capabilities. But tech? That’s where the gap yawns wide.
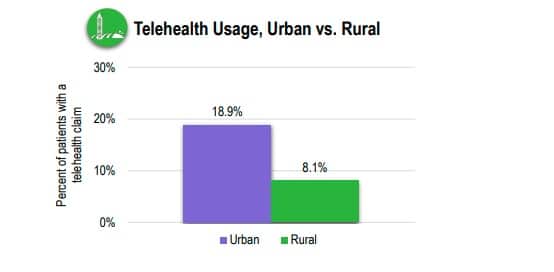
The chart paints a clear picture: telehealth is more widely used in urban areas compared to rural ones. The 18.9% in urban settings suggests better access, due to faster internet, more tech-savvy providers, or a higher concentration of healthcare facilities offering virtual options. Rural areas, at 8.1%, lag behind, which could indicate challenges such as spotty internet connections, fewer providers equipped for telehealth, or lower patient awareness in those regions.
Urban setups thrive on robust networks, integrating AI for everything from appointment reminders to predictive analytics. This tech edge can boost valuations, making city sales more competitive. Yet, rural clinics counter with grit, often partnering with telehealth to bridge gaps.
What challenge is most likely encountered while implementing AI healthcare tools in rural areas? Bandwidth woes top the list; spotty internet in places like Apache County stalls AI diagnostics that urban Phoenix clinics roll out seamlessly.
When selling, highlight those adaptations; buyers love a practice that’s future-proofed on a budget.
4. Financial and Valuation Aspects
Money talks loudest at closing. Clinic location and valuation impact swings wildly here. Rural Arizona clinics often value lower due to thinner patient pools, but their underserved status can draw grants or loan forgiveness perks for buyers. Urban ones command higher tags due to dense demand, although competition clips margins.
Clinic location and valuation impact also hinge on growth potential; a Yuma border clinic might boom with migration trends, outpacing stagnant urban satellites. Savvy sellers bake this into their pitches, turning location from a hurdle to a hook.
Navigating Practice Sale Profitability Factors
Selling isn’t a fire sale; it’s a strategy play. Practice sale profitability factors boil down to revenue streams, patient retention, and ops polish. In rural Arizona, steady Medicaid flows from underserved tags pad profits, but urban clinics bank on private insurance diversity.
Practice sale profitability factors shift with location too: Rural locations, with low overheads, mean quicker ROIs for buyers, while urban locations, with high volumes, promise scale. Teaming up with medical brokers like Strategic Medical Brokers, who know Arizona’s quirks, can smooth the path, connecting you to buyers who get the local pulse.

Sales Dynamics: Rural vs Urban Clinic Transactions in Arizona
Let’s turn to how these operational contrasts affect actual sales in the marketplace, using Arizona as context.
1. Pricing Multiples and Valuation Methods
In medical practice valuation, most buyers use multiples of EBITDA or net income, sometimes adjusted by revenue multiples. The location, patient mix, infrastructure, and risk profile all influence how aggressive or conservative a buyer will be.
Because rural clinics have more uncertainty, buyers often demand higher discount rates. Additionally, the clinic’s location and valuation impact are real: a clinic situated near a growing suburb in the Phoenix metro area may carry more upside than one in a remote county, even if its baseline metrics are lower.
2. Profitability Levers and Margin Risk
One challenge for both rural and urban clinics is controlling fixed costs (rent, staff, regulatory compliance). But rural ones are more vulnerable to small changes in volume, reimbursement cuts, or staff turnover. That means that practice sale profitability factors, such as payor mix, contractual stability, managed care relationships, capital expenditure needs, and historical growth trends, carry extra weight in negotiations.
Buyers often demand warranties or holdbacks tied to post-sale performance in rural deals, more so than in urban ones.
3. Exit timing and incentives
In rural settings, owners may feel pressure to exit earlier due to burnout, isolation, or declining margins. That might give buyers more leverage in negotiations. In urban areas, sellers often have more options and can take time to stage growth before a sale.
This ties into healthcare exit planning. A rural owner who plans to exit too late may see declining value due to infrastructure degradation or staff losses.
4. Competition, Consolidation, and Regional Systems
In cities, buyers may be large health systems or private equity groups consolidating multiple clinics. In rural Arizona, consolidation is more selective, with only a few health systems actively acquiring remote clinics.
But healthcare consolidation pressures exist. Buyers will evaluate how the clinic aligns with a regional strategy, whether it can integrate with a hospital network, and whether its independence is viable. That factor also influences valuation adjustments.
FAQs
Sanford Health leads the pack, a model for how scale aids transitions. Sanford operates many clinics and hospitals across rural states, often with a central strategy to maintain local access while integrating services.
Yes, from a buyer’s perspective, rural clinics carry a higher risk around staff turnover, revenue volatility, connectivity issues, and regulatory changes. Buyers will often demand warranties, holdbacks, or performance contingencies in rural deals.
Yes, but only if you invest first in reliable broadband, upgrade your EHR to be compatible, and build governance around data and compliance. Without that, AI tools may fail or become more of a liability than a help.
Audit your EMR integration now; it uncovers hidden efficiencies that can hike your practice’s appeal to tech-savvy buyers.
Wrap-Up
Rural and urban medical clinic sales in Arizona differ in several fundamental ways: patient density, infrastructure, payer risk, staffing, technology, and growth potential. These differences directly impact clinic location and valuation. Rural clinics face additional hurdles in adopting AI tools, addressing infrastructure gaps, and mitigating staff turnover.
If you are dealing with a medical practice for sale in Arizona, understanding these dynamics can help you negotiate better, plan smarter, and avoid surprises. Connect with us today for clarity, support, and strategic advice every step of the way.







